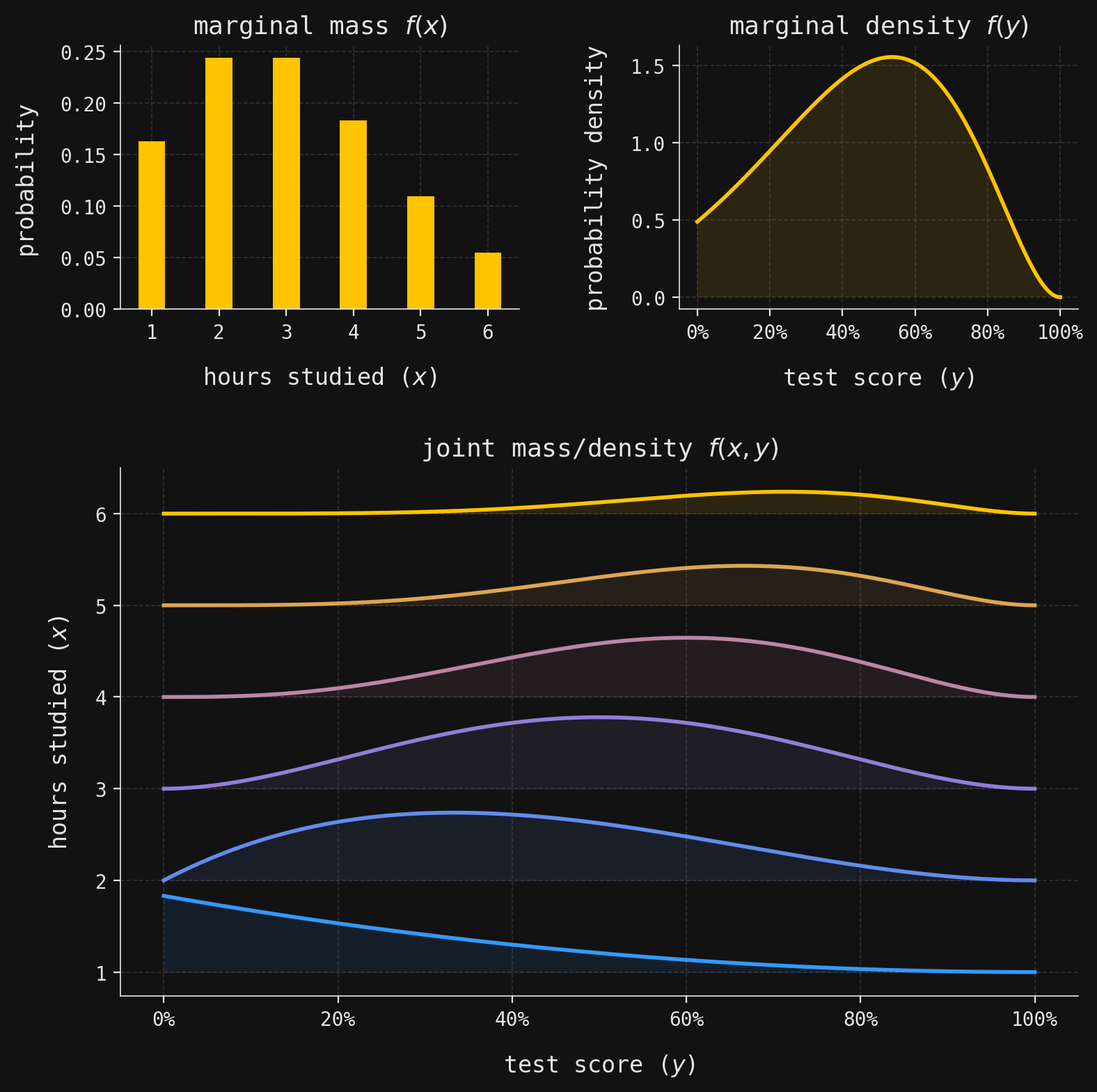
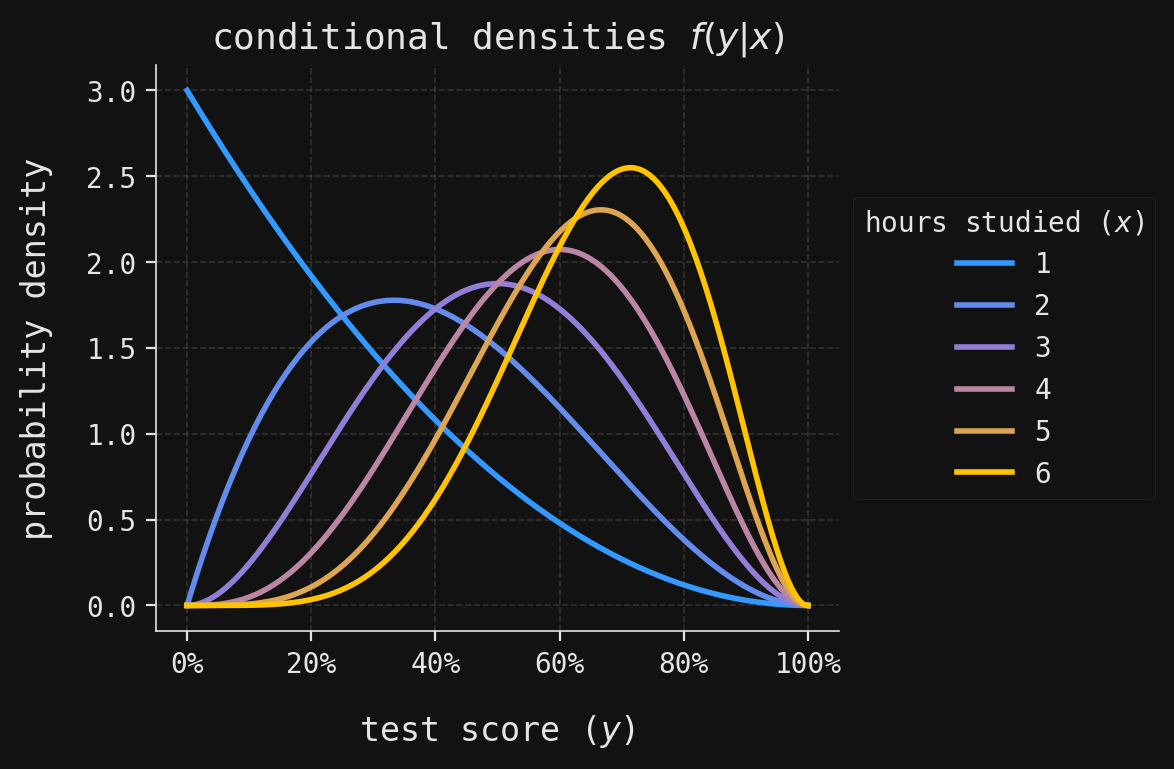
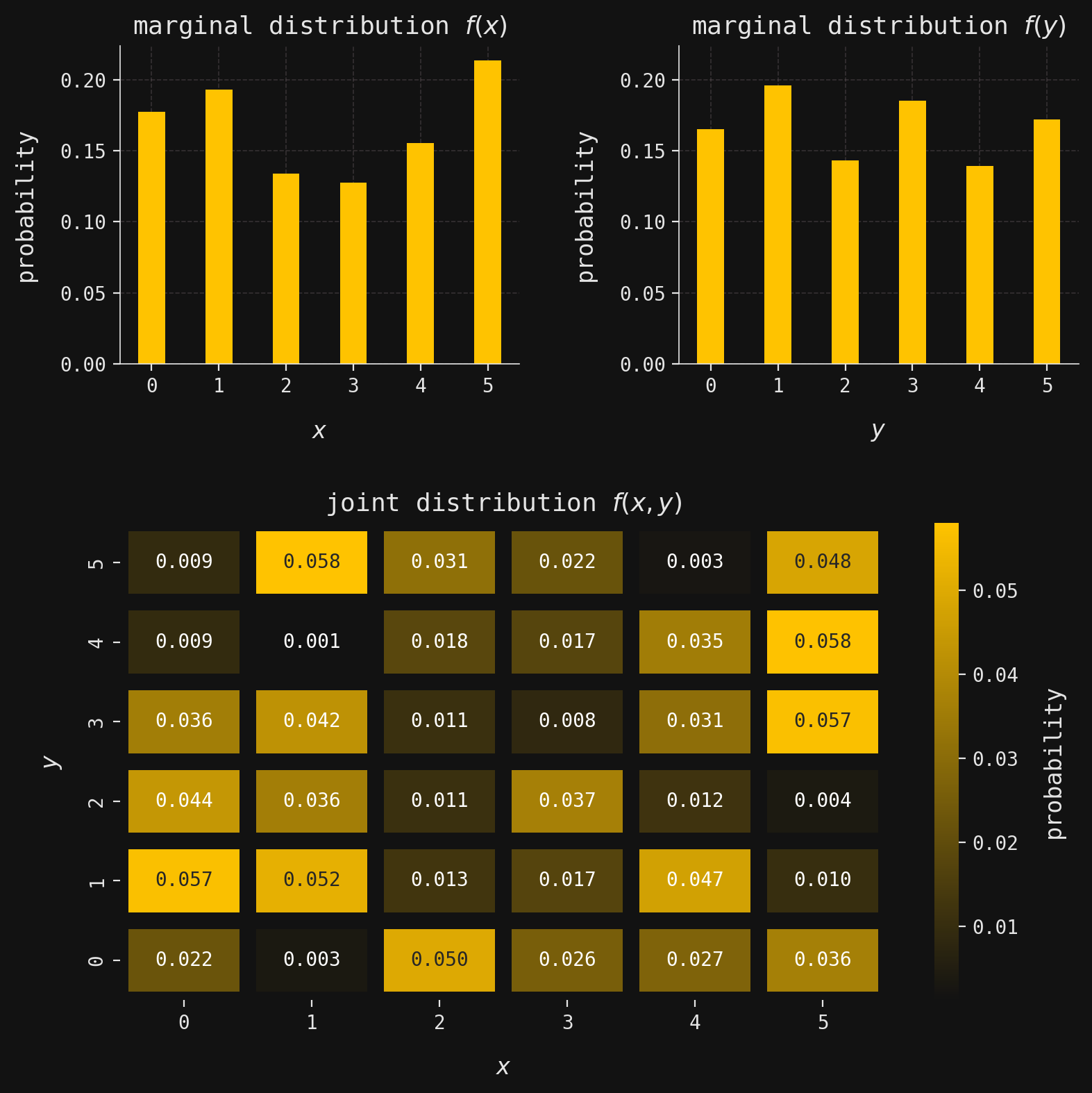
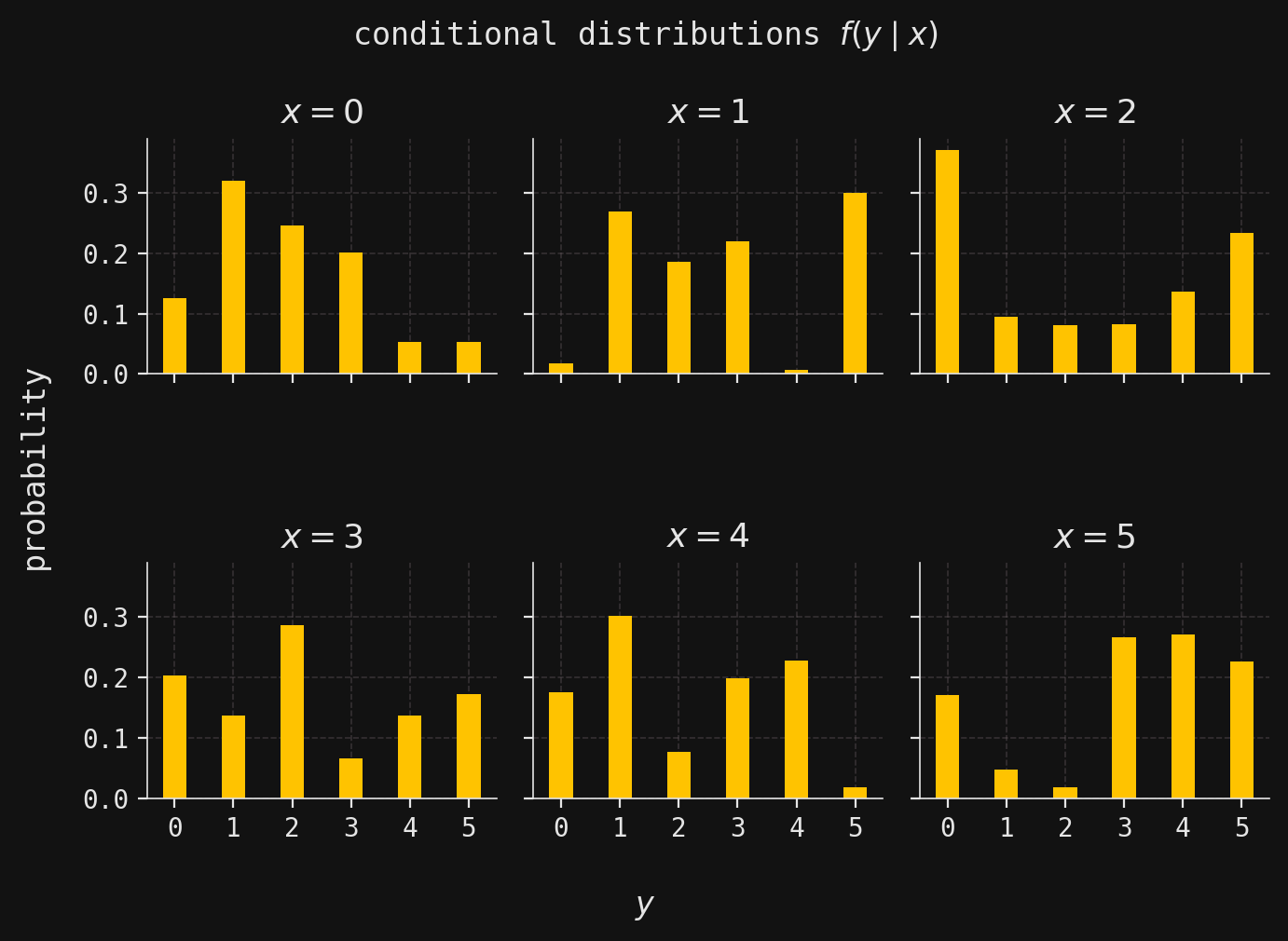
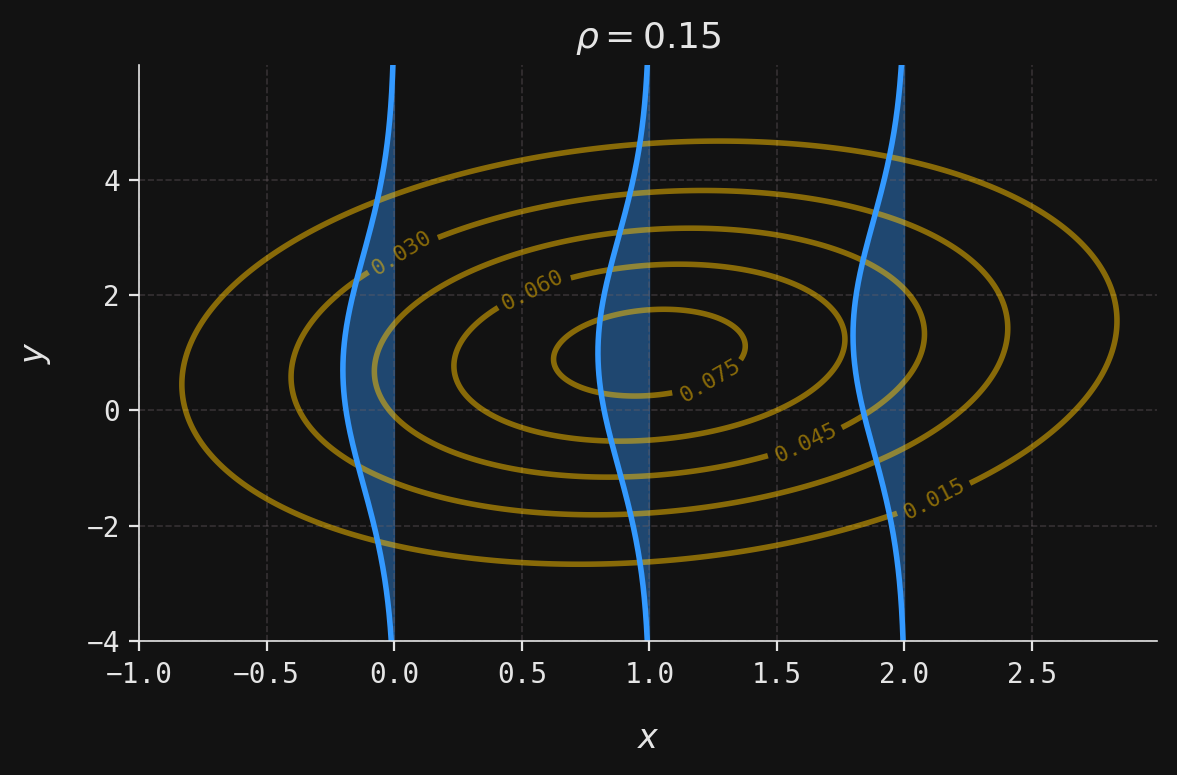
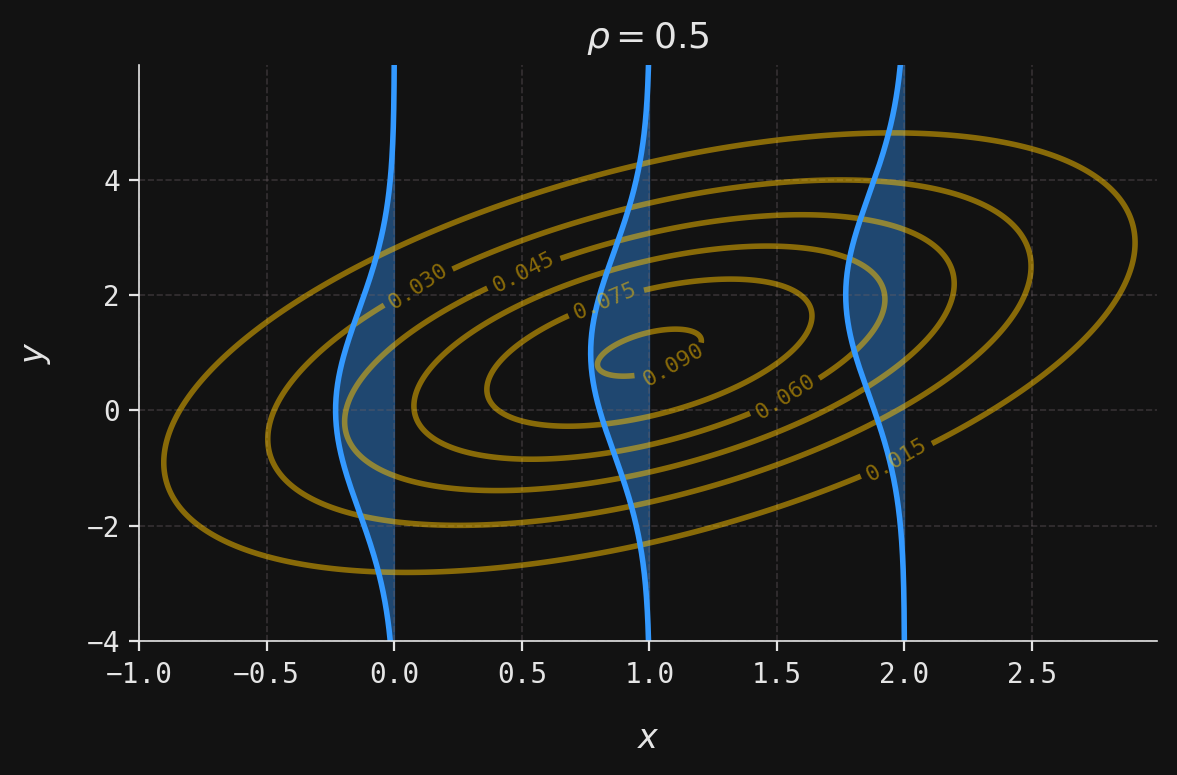
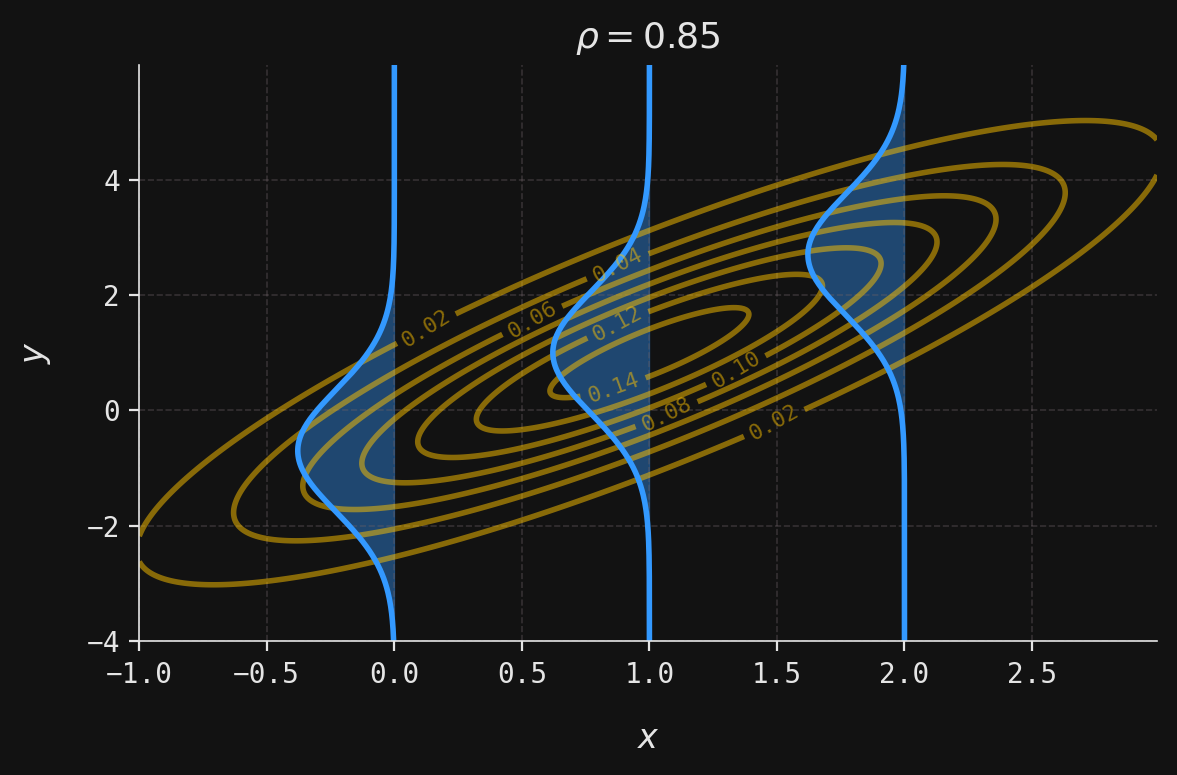
def plot_multivar(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, x, y, labels=False):
Sigma = np.array([[sigmaX ** 2, rho * sigmaX * sigmaY], [rho * sigmaX * sigmaY, sigmaY ** 2]])
Mu = np.array([muX, muY])
U = multivariate_normal(mean=Mu, cov=Sigma)
grid = np.dstack((x, y))
z = U.pdf(grid)
contour = ax.contour(x, y, z, colors=yellow, alpha=0.5)
if labels:
ax.clabel(contour, inline=True, fontsize=8)
def plot_conditional(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, rho, y, x_obs):
mu = muY + (x_obs - muX) * rho * sigmaY / sigmaX
sigma = sigmaY * np.sqrt(1 - rho ** 2)
x = norm(loc=mu, scale=sigma).pdf(y)
ax.plot(-x + x_obs, y, color=blue)
ax.fill_betweenx(y, -x + x_obs, x_obs, color=blue, alpha=0.4)
def plot_combined(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, rho, x, y, x_obs, labels=False):
plot_multivar(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, x, y, labels)
y = np.linspace(np.min(y), np.max(y), num=250)
plot_conditional(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, rho, y, x_obs[0])
plot_conditional(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, rho, y, x_obs[1])
plot_conditional(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, rho, y, x_obs[2])
ax.set_title(rf"$\rho ={rho}$")
ax.set_xlabel(r"$x$")
ax.set_ylabel(r"$y$")
fig = plt.gcf() # Get current figure
fig.set_size_inches(6, 4)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
_, ax = plt.subplots()
x, y = np.mgrid[-1:3:0.01, -4:6:0.01]
muX = 1
muY = 1
sigmaX = 1
sigmaY = 2
rho = 0.15
plot_combined(ax, muX, muY, sigmaX, sigmaY, rho, x, y, x_obs=[0, 1, 2], labels=True)